
- #HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP HOW TO#
- #HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP INSTALL#
- #HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP FULL#
- #HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP DOWNLOAD#
With this handy tool, you can be up and running with two of the most important technology building blocks on the market. Thanks to Docker Desktop, getting both Docker and Kubernetes up and running on your Mac doesn’t have to be a barrier to entry. Of course, if you are serious about learning both Docker and Kubernetes, you should probably make yourself at home with the command line as well. With the likes of Kubernetic, you can easily create Pods, Services, Ingresses, Deployments and more, all without having to open a terminal window.
#HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP INSTALL#
Simply install a third-party GUI tool and you’re ready to start working with your instance of Kubernetes. The good news is, since you have Kubernetes already running on your Mac, the hard part is taken care of.
#HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP DOWNLOAD#
Download an image you want to work with, modify it to suit your needs and deploy.Īs for Kubernetes, it is all handled via the command line, unless you install a third-party tool (such as Kubernetic). You can now start working with images and deploying containers, all from a handy GUI tool. In the resulting window ( Figure C), click on the Kubernetes tab. To do this, click the Docker Desktop icon and select Preferences. Installing Kubernetesįor our next trick, we’ll install Kubernetes support for Docker Desktop. Use your Docker Hub account credentials in order to link Docker Desktop to your repositories. Once that file is downloaded, open Finder, navigate to the folder housing the file, double-click the installation, and walk through the simple instructions.Īt this point, make sure to click the Docker Desktop icon and click the Sign-in entry. Instead, download the latest version of Kitematic from GitHub. Although there is an entry in the Docker Desktop menu for Kitematic installation, don’t use it as it will not result in a successful installation. Once Git is installed, you can install Kitematic.
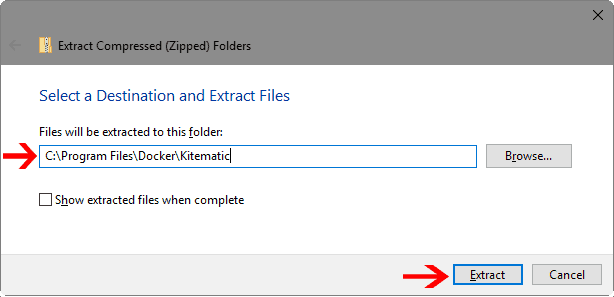

Once downloaded, open Finder, navigate to the folder housing the file, double-click the installer, and walk through the easy-to-follow instructions. In order to install Git, download the installer. Before you can install Kitematic, you must first install Git. Installing Kitematicįor those who’d prefer not to have to rely solely on the command line, there is the Kitematic GUI. You’re now ready to install a few more components. When the Docker window opens ( Figure A), click and drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder. Locate and double-click the Docker.dmg file. Once that file is saved on your drive, open Finder and navigate to the folder housing the download. The first thing to do is download the Docker Desktop.
#HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP HOW TO#
Let’s find out how to install this must-have tool for macOS container developers.
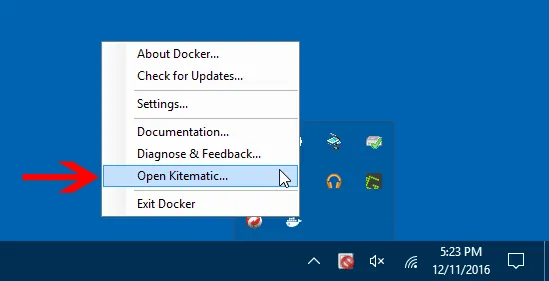
#HOW TO START KITEMATIC ON DOCKER DESKTOP FULL#
Once installed, you’ll have quick access to Docker Hub repositories, the full complement of Docker commands, easy installation of Kitematic (a GUI for container management), and even Kubernetes if you wish to do some testing or just learn how Kubernetes works. Thanks to the developers of Docker Desktop, getting both Docker and Kubernetes up and running on your platform of choice is incredibly simple.

You’re in luck, as there’s a macOS GUI for that very purpose. But what about macOS? Does the installation of these two tools require opening a terminal window and working with numerous (and sometimes complicated) commands? If you’ve ever attempted to install Kubernetes on Linux, you know it’s not a point and click affair. It’s solid, runs on some of the best hardware on the market, and integrates with peripherals and devices like no other.īut for many macOS users, the idea of installing Docker and Kubernetes, might be a bit daunting. One such platform that is often seen as an ideal developer environment is Apple’s macOS. Although Linux might be the foundation for which most enterprise-level businesses are built, it takes a village of platforms to keep it going.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
